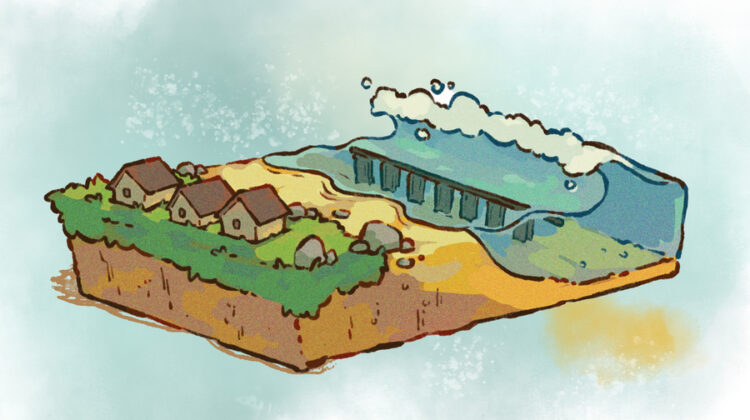

A team of engineers at MIT is hoping to fortify coastlines with ‘architected’ reefs – sustainable, offshore structures designed to mimic the wave-buffering effects of natural reefs while also providing pockets for fish and other marine life.
Coral reefs serve as both a marine refuge and natural buffer against stormy seas. But as the effects of climate change bleach and break down coral reefs around the world, and extreme weather events become more common, coastal communities are left increasingly vulnerable to frequent flooding and erosion.
The team’s reef design centres on a cylindrical structure surrounded by four rudder-like slats. The engineers found that when this structure stands up against a wave, it efficiently breaks the wave into turbulent jets that ultimately dissipate most of the wave’s total energy. The team has calculated that the new design could reduce as much wave energy as existing artificial reefs using ten times less material.
The researchers plan to fabricate each cylindrical structure from sustainable cement, which they will mould in a pattern of ‘voxels’ that could be automatically assembled, and would provide pockets for fish to explore and other marine life to settle in. The cylinders could be connected to form a long, semipermeable wall, which the engineers could erect along a coastline, a bit less than a kilometre from shore. Based on the team’s initial experiments with lab-scale prototypes, the architected reef could reduce the energy of incoming waves by more than 95 per cent.
‘This would be like a long wave-breaker,’ said Michael Triantafyllou, the Henry L and Grace Doherty professor in ocean science and engineering in the Department of Mechanical Engineering. ‘If waves are six metres high coming toward this reef structure, they would be ultimately less than a metre high on the other side. So, this kills the impact of the waves, which could prevent erosion and flooding.’
Some regions have already erected artificial reefs to protect their coastlines from encroaching storms. These structures are typically sunken ships, retired oil and gas platforms, and even assembled configurations of concrete, metal, tires and stones. However, there’s variability in the types of artificial reefs that are currently in place, and no standard for engineering such structures. What’s more, the designs that are deployed tend to have a low wave dissipation per unit volume of material used. That is, it takes a huge amount of material to reduce wave energy enough to adequately protect coastal communities.
The MIT team instead looked for ways to engineer an artificial reef that would efficiently dissipate wave energy with less material, while also providing a refuge for fish living along any vulnerable coast. ‘Remember, natural coral reefs are only found in tropical waters,’ said Triantafyllou. ‘We cannot have these reefs, for instance, in Massachusetts. But architected reefs don’t depend on temperature, so they can be placed in any water, to protect more coastal areas.’
The new effort is the result of a collaboration between researchers in MIT Sea Grant, who developed the reef structure’s hydrodynamic design, and researchers at the Center for Bits and Atoms (CBA), who worked to make the structure modular and easy to fabricate on location.
The team’s architected reef design grew out of two seemingly unrelated problems. CBA researchers were developing ultralight cellular structures for the aerospace industry, while Sea Grant researchers were assessing the performance of blowout preventers in offshore oil structures – cylindrical valves that are used to seal off oil and gas wells and prevent them from leaking.
The latter team’s tests showed that the structure’s cylindrical arrangement generated a high amount of drag. In other words, the structure appeared to be especially efficient at dissipating high-force flows of oil and gas. They wondered whether the same arrangement could dissipate the flow of ocean waves.
The researchers began to play with the general structure in simulations of water flow, tweaking its dimensions and adding certain elements to see whether and how waves changed as they crashed against each simulated design. This iterative process ultimately landed on an optimised geometry: a vertical cylinder flanked by four long slats, each attached to the cylinder in a way that leaves space for water to flow through the resulting structure. They found this setup essentially breaks up any incoming wave energy, causing parts of the wave-induced flow to spiral to the sides rather than crashing ahead.
Once the researchers identified an optimal wave-dissipating structure, they fabricated a laboratory-scale version of an architected reef made from a series of the cylindrical structures, which they 3D-printed from plastic. Each test cylinder measured about 30 centimetres wide and 1.2 metres tall. They assembled a number of cylinders, each spaced about 30 centimetres apart, to form a fence-like structure, which they then lowered into a wave tank at MIT. They then generated waves of various heights and measured them before and after passing through the architected reef. ‘We saw the waves reduce substantially, as the reef destroyed their energy,’ Triantafyllou said.
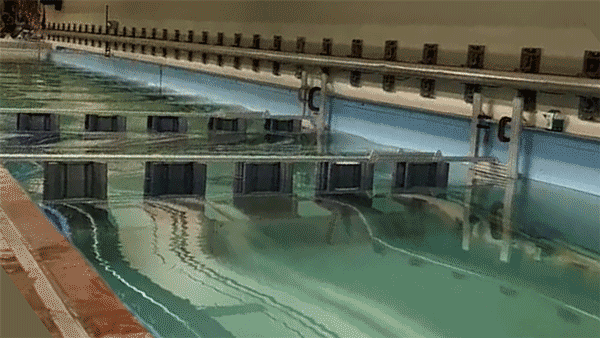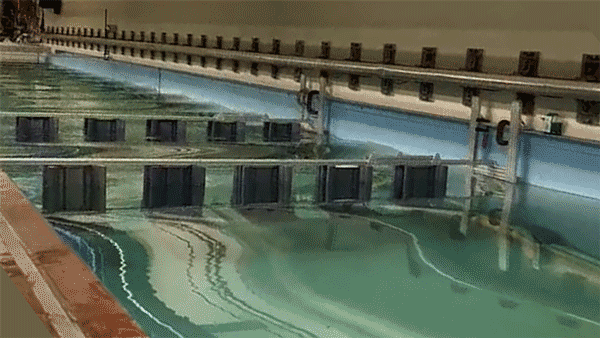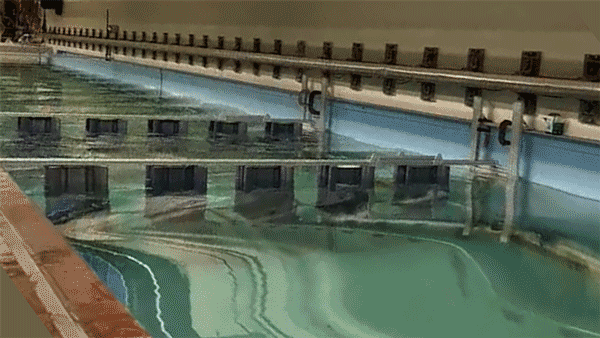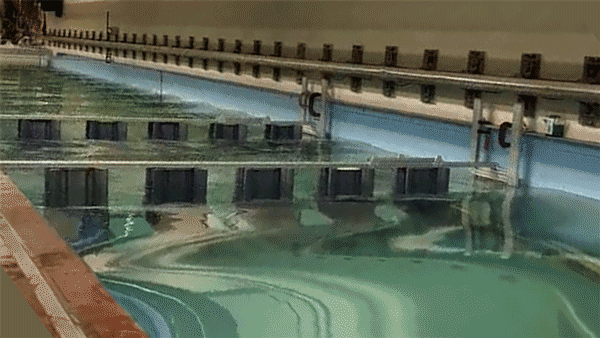
The team has also looked into making the structures more porous and friendly to fish. They found that, rather than making each structure from a solid slab of plastic, they could use a more affordable and sustainable type of cement. ‘We’ve worked with biologists to test the cement we intend to use and it’s benign to fish, and ready to go,’ he added.
They identified an ideal pattern of ‘voxels,’ or microstructures, that cement could be moulded into, in order to fabricate the reefs while creating pockets in which fish could live. This voxel geometry resembles individual egg cartons, stacked end to end, and appears to not affect the structure’s overall wave-dissipating power.
The team is currently fabricating cement voxel structures and assembling them into a lab-scale architected reef thar they will test under various wave conditions. They envision that the voxel design could be modular and scalable to any desired size, and easy to transport and install in various offshore locations. ‘Now we’re simulating actual sea patterns, and testing how these models will perform when we eventually have to deploy them,’ said Anjali Sinha, a graduate student at MIT who recently joined the group.
Going forward, the team hopes to work with beach towns in Massachusetts to test the structures on a pilot scale.
‘These test structures would not be small,’ Triantafyllou emphasised. ‘They would be about a mile (1.6 kilometres) long and about five metres tall, and would cost something like US$6million per mile (US$3.75million per kilometre). So it’s not cheap, but it could prevent billions of dollars in storm damage. And with climate change, protecting the coasts will become a big issue.’
The research has been published in PNAS Nexus.



